This report is an analysis of IAM activities undertaken by the threat actor in the LastPass breach; the source of this analysis is the publicly reported incident timeline from LastPass.
Introduction to the Analysis of the LastPass Cloud Data Breach
This report is a bit different from other traditional breach and incident analysis reports in that it is focused on analyzing the incident from a perspective of IAM (Identity Access and Management) flows. With every cloud breach, it becomes clearer that having a comprehensive understanding of who can access what information is crucial. Complete and contextual visibility over identity and access controls enables cloud operations and security teams to fully manage the risk of unauthorized access, making identity and access fully controllable.
The goal of this analysis is focused on the IAM perspective of the incidents that occurred. This is important because:
- Identity and Access Management is the “lynchpin cloud service” that every other cloud service depends upon. No entity or identity can take any action in the cloud without IAM.
- Threat actors always leave a cloud IAM footprint in the wake of their enumeration and lateral movement activities.
Analysis of LastPass Cloud Data Breach and Relevant Shadow Access Problems
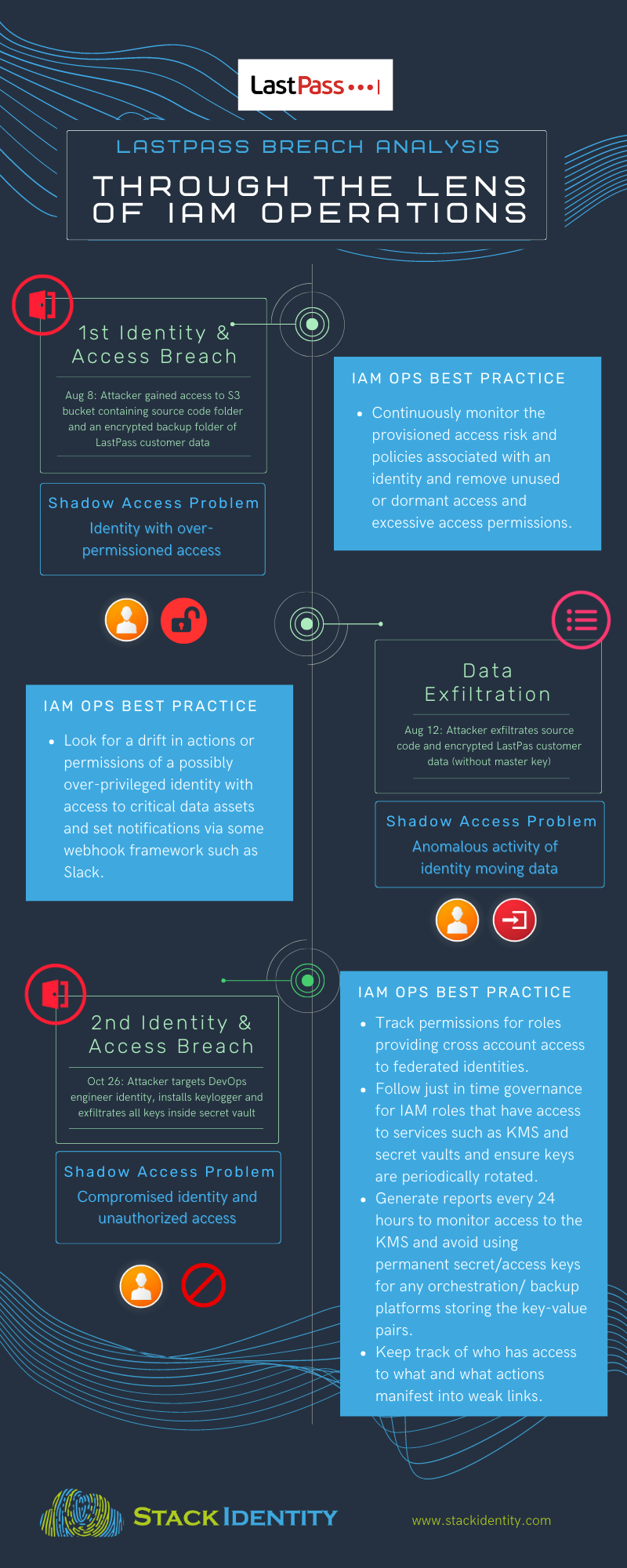
The following is an analysis of the LastPass DataBreach, outlining IAM Operational gaps that result in Shadow Access problems that enabled each incident/activity.
| Timeline | Incident/Activity | Shadow Access Problem that Enabled Incident/Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Aug 8, 2022 |
1st Identity and Access Breach: Attacker gained access to an S3 bucket containing a) source code folder and b) encrypted backup folder of LastPass customer data.
This was accomplished through an anonymous VPN that bypassed endpoint detection and response capabilities. Specifically, the attacker leveraged permissions which were never used before by the over-permissioned identity giving it overly-scoped access to folders, including the backup folder of LastPass customer data. |
Identity with over-permissioned access used to access data in the cloud. |
| Aug 12, 2022 |
Data Exfiltration: External party exfiltrated source code folder and encrypted backup folder of LastPass customer data stored in the same S3 bucket. Note: the master key for decrypting the data was not available to the over- permissioned identity used to access the folder. |
Inability to detect anomalous activity of over-permissioned identity moving data. |
| Aug 12, 2022 | Suspicious Access Activity Detected and Incident Investigation Initiated | Inability to quickly detect incidents of access breach and data exfiltration. |
| Aug 13, 2022 |
Incident Investigation: Investigation found that access occurred through an anonymous VPN gateway and anti-evasion tools were used to bypass EDR tools. Report was submitted and the incident closed. It is unclear whether the identity used to breach access was still in the system, possibly leaving access open. |
Lack of visibility of over-permissioned identity still active/dormant in the system with access to cloud systems. |
| Oct 26, 2022 |
2nd Identity and Access Breach The attacker then targeted one of the 4 DevOps engineers and installed a keylogger that captured the master key and then proceeded to exfiltrate all the keys inside the secret vault. |
Lack of visibility of compromised DevOps identity and unauthorized access. |
For each incident or activity in the timeline of the LastPass data breach, visibility and control of identity and access management in the cloud was the pivotal capability that enabled all further activities (lateral movement, data exfiltration, key logger) by the attacker.
Recommended Best Practices to Prevent Cloud Data Breaches Such As LastPass
Reviewing the timeline of incidents and attacker activity Stack Identity recommends the following best practices to quickly detect and remediate unauthorized, unmonitored and invisible shadow access, thereby preventing the initiation of the entire sequence of events.
| Timeline | Incident/Activity | Recommended IAM Operations Best Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Aug 8, 2022 | 1st Identity and Access Breach: External party gained access to the S3 bucket containing two folders, 1) source code, and 2) encrypted backup folder of LastPass customer data. |
|
| Aug 12, 2022 | Data Exfiltration: External party exfiltrates source code and the encrypted backup folder of LastPass customer data. |
|
| Oct 26, 2022 | 2nd Identity and Access Breach
The attacker targeted one of the 4 DevOps engineers whose meta data was available from the initial incident, and proceeded to exfiltrate all the keys inside the secret vault. |
|
Collectively; IAM Risks, vulnerabilities, threats and operational gaps have a huge and critical impact on modern cloud data breaches and incidents. Yet, the IAM operational dimension is not viewed with a level of criticality and relevance. Incident after incident calls out IAM as a bullet or a footnote in the forensics analysis. This much is certain. When there are several thousands of APIs and programmatic ways to acquire and elevate access means it’s only a matter of time before access is breached.
Our goal is to call attention to this IAM dimension and learn via these breaches what can be done differently to strengthen Cloud IAM Operations to mitigate this risk.